Kiểm tra tải pin là gì?
Battery load testing is a diagnostic method for evaluating a battery’s ability to deliver power under real-world operating conditions. It involves applying a controlled electrical load to the battery and observing how the battery’s điện áp và dòng điện đầu ra respond. In essence, the test simulates the demands of actual usage – such as starting a car engine or powering a device – and checks whether the battery can maintain an adequate voltage when under load. This is a more stringent test than a simple open-circuit voltage check, since a battery can appear fully charged at rest but không cung cấp thời gian chạy mong đợi khi tải. By performing a load test, engineers and technicians can measure key performance indicators like the voltage drop and internal resistance (which reflects the battery’s capability to supply current). These indicators reveal the true health of the battery and help identify weak or aging batteries before they lead to failure in the field.

Kiểm tra tải pin được sử dụng rộng rãi trong các ngành công nghiệp mà độ tin cậy của pin là rất quan trọng. Thợ máy ô tô kiểm tra tải pin ô tô (đặc biệt là trong các tình huống khởi động nguội) để đảm bảo chúng có thể cung cấp đủ dòng điện để khởi động động cơ. Trong các hệ thống lưu trữ năng lượng tái tạo và nguồn điện dự phòng, kiểm tra tải xác nhận rằng các cụm pin sẽ hỗ trợ các tải quan trọng trong thời gian mất điện. Nhà sản xuất of batteries and devices also use load tests for quality control – to verify that new battery packs meet their specifications for capacity and output. In consumer electronics and industrial power systems, routine load testing helps catch performance issues early, preventing unexpected downtime or data loss due to a dying battery.
Tại sao kiểm tra tải pin lại quan trọng?
Kiểm tra tải pin đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc bảo trì, an toàn và đảm bảo hiệu suất của pin. Một số lý do chính bao gồm:
- Kiểm soát chất lượng (Nhà sản xuất): Áp dụng thử nghiệm tải trong quá trình sản xuất đảm bảo pin đáp ứng các thông số kỹ thuật thiết kế và tiêu chuẩn chất lượng. Nó giúp phát hiện sớm các lỗi sản xuất hoặc mất cân bằng cell, ngăn ngừa pin kém chất lượng tiếp cận thị trường. Điều này cải thiện độ tin cậy chung của sản phẩm và giảm khiếu nại bảo hành.
- Độ tin cậy cho người dùng cuối: For businesses and individuals who rely on batteries, load testing is crucial to verify that a battery will perform when it’s needed most. For example, backup power systems in telecom or data centers are routinely load-tested to validate battery capacity and runtime. This process can uncover weak cells or wiring issues trước they cause unplanned downtime. By identifying a declining battery in an electric vehicle, solar storage bank, or UPS system, it can be replaced proactively – avoiding sudden failures and ensuring continuous operation.
- Tối ưu hóa hiệu suất và tuổi thọ: Regular load testing helps in tracking a battery’s available capacity and internal resistance over time. By comparing test results against the battery’s rated capacity, users can determine when the battery has aged significantly. This information allows for optimized charging schedules and timely maintenance. Keeping batteries “exercise tested” under load can also prevent capacity loss from long periods of inactivity, thereby extending their usable lifespan.
- An toàn và tuân thủ: Faulty or deteriorating batteries can pose safety risks such as overheating, leakage, or in extreme cases (particularly with lithium-ion chemistries) thermal runaway. Load testing under controlled conditions can reveal these issues early, so that unsafe batteries are removed from service. Moreover, many industry standards and transportation regulations require rigorous battery testing. For instance, virtually all lithium-ion batteries must pass the UN 38.3 safety tests – a series of abuse and load conditions – to be certified for transport. Systematically load-testing battery systems helps ensure compliance with such standards and gives confidence that batteries can withstand the stresses of actual use.
Nguyên tắc kiểm tra tải pin
Về cơ bản, thử nghiệm tải pin hoạt động theo nguyên tắc đơn giản: apply a known load and measure the battery’s response. By observing how much the voltage drops under load and how well the battery sustains the load current, one can infer the battery’s internal condition. A healthy battery will maintain a higher voltage and recover quickly after the test, whereas a weak battery’s voltage will sag significantly under load and may struggle to recover afterward. The amount of voltage drop is directly related to the battery’s internal resistance – lower internal resistance means the battery can deliver higher current with less voltage drop.

Trong quá trình thử tải, nhiều thông số khác nhau được theo dõi chặt chẽ: sụt áp trên pin khi tải được áp dụng, hiện hành flowing, and often the battery’s nhiệt độ trong quá trình thử nghiệm. Điện áp giảm đáng kể hoặc tỏa nhiệt bất thường có thể chỉ ra điện trở bên trong tăng hoặc hư hỏng cell. Ngược lại, pin trong tình trạng tốt sẽ chỉ cho thấy điện áp giảm nhẹ và ít tỏa nhiệt đối với tải được chỉ định.
Hành vi của pin khi chịu tải cũng phụ thuộc vào thành phần hóa học và thiết kế của nó. Các loại pin khác nhau có đặc điểm xả riêng biệt. Ví dụ, pin axit chì có xu hướng thể hiện mức sụt điện áp lớn hơn và mất dung lượng hiệu dụng ở tốc độ xả cao, trong khi pin lithium-ion (đặc biệt là Lithium Iron Phosphate, LiFePO4) duy trì điện áp ổn định hơn và cung cấp tỷ lệ phần trăm dung lượng cao hơn ngay cả khi chịu tải nặng. Điều này có nghĩa là pin lithium thường xử lý dòng điện cao tốt hơn pin axit chì có định mức tương đương.
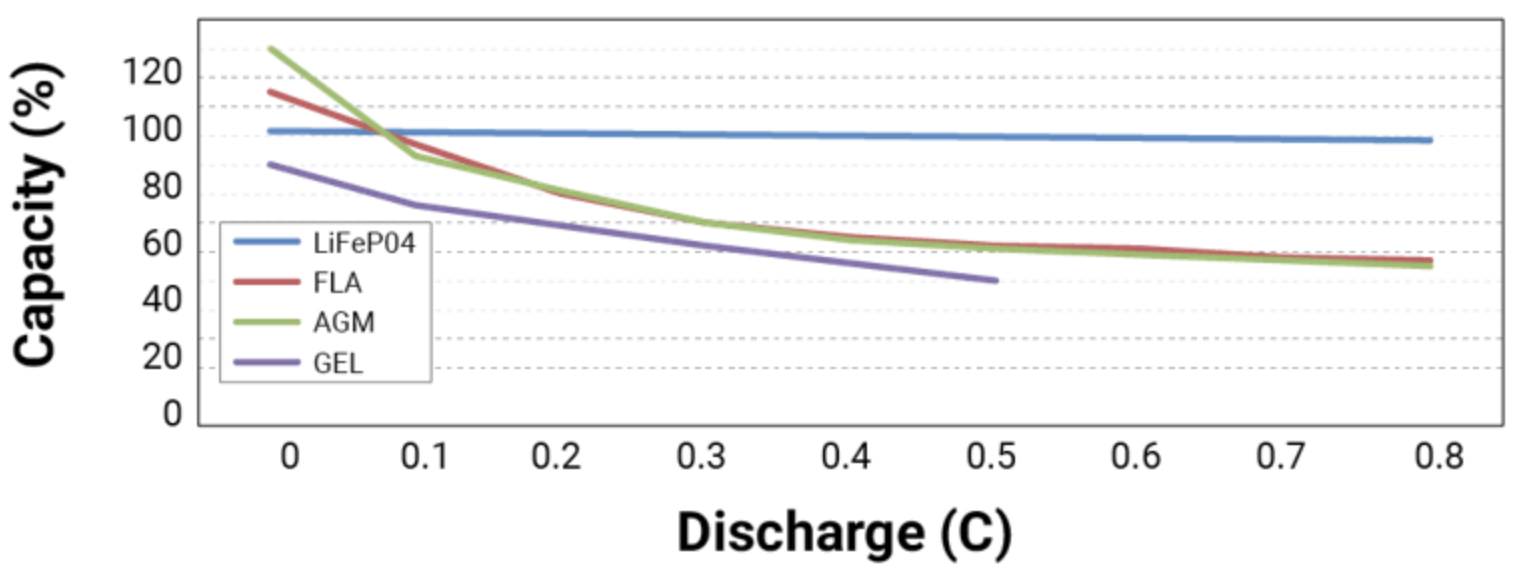
Hiểu được những khác biệt về hóa học này là điều quan trọng khi giải thích kết quả thử tải. Sự sụt giảm điện áp có thể là bình thường đối với một loại pin có thể báo hiệu sự cố ở loại pin khác. Tương tự như vậy, nhẹ Có thể dự đoán dung lượng sẽ giảm theo thời gian đối với pin axit chì được sử dụng nhiều, trong khi một bộ pin Li-ion được quản lý tốt sẽ giữ được hầu hết dung lượng của nó qua cùng số chu kỳ.
Nhiệt độ is another critical factor influencing load testing. Batteries perform best around room temperature, and both cold and hot conditions can skew test outcomes. In cold environments, a battery’s internal resistance increases and its ability to deliver current decreases – effectively reducing its available capacity. For instance, a battery that provides full capacity at about 27 °C (80 °F) might only deliver roughly 50% of its capacity at –18 °C (0 °F). Importantly, this capacity loss in the cold is usually tạm thời: một khi pin được làm ấm trở lại nhiệt độ bình thường, hiệu suất của nó nói chung phục hồi về mức trước đó. Because of this, load tests are usually conducted at standardized temperatures (around 20–25 °C, unless the goal is to specifically test cold/hot performance) to ensure the results reflect the battery’s true health rather than a transient thermal effect.
Để có được dữ liệu chính xác và có ý nghĩa, thử nghiệm tải tuân theo một bộ các thông lệ tốt nhất. Pin thường là đã được kiểm tra khi sạc đầy and in a rested state (no recent charging or discharging that could skew the voltage). The load applied should be chosen to mimic the battery’s real-world application – for example, drawing a high burst current to simulate a power tool or vehicle starter, or a steady lower current to simulate a device drain. The test is run for a defined duration long enough to observe the battery’s behavior (but usually short enough to avoid completely depleting the battery or causing undue stress). Throughout the test, conditions are kept controlled: the ambient temperature is kept stable, and the test equipment (load banks, meters, etc.) is đã hiệu chuẩn for accuracy. Following these principles ensures that the load test results can be reliably compared to manufacturer specifications and previous test results, giving a clear picture of the battery’s state of health.
Các loại thử nghiệm tải pin
Có một số loại thử nghiệm tải pin, mỗi loại phù hợp với các mục đích và hệ thống pin khác nhau:
- Kiểm tra tải dòng điện không đổi: A steady, fixed current is drawn from the battery for a specified period. By measuring how the battery’s voltage declines over time under this constant load, one can assess its capacity and voltage stability. This is a common method to determine a battery’s true amp-hour capacity – for example, discharging at a 1 C rate (equal to the battery’s rated capacity) and seeing how long it sustains the load before reaching a cutoff voltage.
- Kiểm tra tải xung: The battery is subjected to intermittent high-current pulses separated by rest periods. This tests the battery’s response to sudden power demands. The voltage is monitored during each pulse to see how well it recovers in the brief rest. Pulse testing is often used to evaluate starting batteries or batteries in devices that periodically draw bursts of current. It can also help estimate internal resistance and dynamic performance without fully discharging the battery.
- Kiểm tra dung lượng (thời gian chạy): Về cơ bản, đây là một thử nghiệm xả hoàn toàn có kiểm soát. Pin được xả ở tốc độ đã đặt (có thể là dòng điện không đổi hoặc mô hình sử dụng được mô phỏng) cho đến khi đạt đến ngưỡng ngắt (điện áp an toàn tối thiểu). Tổng thời gian hoặc tổng năng lượng được cung cấp được đo. Điều này cho thấy công suất sử dụng của pin và cung cấp phép đo trực tiếp thời gian chạy trong những điều kiện đó. Các thử nghiệm như vậy hữu ích để kiểm tra xem pin có còn giữ được mức sạc dự kiến hay không. Ví dụ, chuỗi pin UPS có thể được thử nghiệm xả để đảm bảo nó có thể chịu được tải trong khoảng thời gian cần thiết (ví dụ 30 phút) trước khi điện áp giảm quá thấp.
- Kiểm tra tải quay: Used primarily for automotive and lead–acid starter batteries, this test measures the battery’s ability to deliver a very high current for a short duration (as needed to crank an engine). A specialized load tester or carbon pile applies a heavy load (hundreds of amps for a car battery) for 5–10 seconds while monitoring the voltage. The voltage should stay above a specified threshold (e.g. ~9.6 V for a 12 V battery at room temperature, higher if tested warm) during the crank simulation. A battery that cannot maintain voltage under this brief but intense load is likely failing, even if it reads 12 V in open-circuit. Cranking tests are often part of car battery diagnostics, especially in cold weather, to ensure reliable starts.
Thiết bị kiểm tra tải pin
Thực hiện thử tải an toàn và chính xác đòi hỏi phải có thiết bị phù hợp. Các công cụ và thành phần chính bao gồm:
- Kiểm tra tải / Ngân hàng tải: This is the device that actually puts a controlled load on the battery. Simple portable load testers for car batteries use a resistor or carbon pile to draw a high current. More advanced electronic load banks can be programmed to draw specific currents or profiles and often include built-in meters. The load tester typically measures the battery’s voltage under load, and some models also measure internal resistance and other metrics.
- Đồng hồ vạn năng hoặc vôn kế: A calibrated multimeter is used to independently measure the battery’s voltage and sometimes current during testing. This provides accurate readings and a sanity check against the load tester’s built-in measurements. In some cases, clamp ammeters are also used to verify the exact current being drawn.
- Máy ghi dữ liệu/Máy phân tích pin: For more detailed testing (especially in research, manufacturing, or predictive maintenance), data acquisition devices record the battery’s voltage, current, and temperature throughout the load test. The resulting data can be analyzed to see how quickly the voltage declines, how stable the current draw remained, and if there were any irregular drops or recoveries. This is useful for comparing multiple batteries or tracking a battery’s performance over time.
- Cảm biến nhiệt độ: Because temperature greatly affects battery behavior, testers often monitor ambient and battery temperature. In critical testing, thermocouples might be attached to the battery to ensure it’s within the desired temperature range and to detect any dangerous overheating during the test.
- Thiết bị an toàn: Kiểm tra tải có thể gây căng thẳng cho pin, vì vậy an toàn là trên hết. Nên đeo đồ bảo hộ như găng tay cách điện và kính bảo vệ mắt, đặc biệt là với pin lớn hơn có thể giải phóng tia lửa hoặc chất điện phân nếu có sự cố xảy ra. Cần thông gió thích hợp khi kiểm tra pin axit chì (có thể phát ra khí hydro) và nên có phương tiện chữa cháy khi kiểm tra pin lithium năng lượng cao. Ngoài ra, việc sử dụng cáp và kẹp định mức chính xác cho tải là rất quan trọng để tránh chúng bị quá nhiệt trong quá trình kiểm tra dòng điện cao.
Quy trình kiểm tra tải pin
When you are ready to conduct a battery load test, it’s important to follow a structured process:
- Sự chuẩn bị: Begin with a fully charged battery. Make sure the battery has been rested for a while after charging so that the voltage has stabilized (surface charge dissipated). Check the ambient conditions – ideally, test in a room-temperature environment unless you are specifically evaluating cold or hot performance. Gather all required equipment (load tester, multimeter, etc.), and put on appropriate safety gear. Also, review the battery’s specifications to know what load and voltage values to expect (for example, maximum test current or minimum allowable voltage).
- Kết nối thiết bị: Turn off or set the load tester to zero before connecting. Attach the load tester’s leads to the battery terminals: positive (+) to positive, negative (–) to negative, ensuring solid connections. If using a separate voltmeter or data logger, connect those probes or sensors to the battery as well. Double-check all connections are secure to avoid arcing when the test begins.
- Thiết lập các thông số tải: Configure the load tester to the desired load. This could mean dialing in a certain current (e.g. a 50 A draw for a small battery, or a 300 A draw for a car battery test), or selecting a specific test mode on an electronic load (constant current, pulse, etc.). Refer to the battery’s ratings or the relevant standard for guidance – for instance, use a load equal to half the battery’s CCA rating for an automotive load test, or a 0.2 C (5-hour rate) load for a capacity test, depending on the goal.
- Thực hiện bài kiểm tra: Kích hoạt máy kiểm tra tải để bắt đầu rút dòng điện từ pin. Duy trì tải trong khoảng thời gian quy định. Có thể chỉ mất vài giây cho thử nghiệm dòng điện cao hoặc có thể mất vài phút hoặc vài giờ cho thử nghiệm xả kéo dài (trong trường hợp này, hãy đảm bảo tải không đổi hoặc tuân theo hồ sơ yêu cầu). Monitor the battery’s behavior throughout. Observe the voltage reading – a sharp drop initially is normal, but it should stabilize above the minimum acceptable voltage. Watch for any signs of distress such as the battery overheating, smoking, or emitting unusual odors (if so, terminate the test immediately). If using a data logger, ensure it’s recording properly.
- Theo dõi và phân tích kết quả: Once the test interval is completed, remove or turn off the load. Continue to watch the battery’s voltage recovery for a minute or two. Note the loaded voltage and the recovery voltage. Now analyze the data: Did the battery maintain voltage above the cutoff threshold during the test? How much capacity (Ah or minutes of runtime) was delivered in a full discharge test? Compare these outcomes to the battery’s rated specifications or to previous test results. A healthy battery should meet or come close to its specs (e.g. delivering its rated amp-hours, or keeping above the minimum voltage under load). If the battery’s performance falls short, it may indicate aging or damage. Use this information to decide on next steps – for example, keep the battery in service with a scheduled re-test later, or retire/replace the battery if it failed to perform.
Giải thích kết quả thử tải
Hiểu được kết quả của thử nghiệm tải pin cũng quan trọng như việc thực hiện thử nghiệm. Sau đây là những khía cạnh chính cần xem xét khi diễn giải kết quả:
- Phản ứng điện áp: Observe how the battery’s voltage behaved under load. A điện áp ổn định that stays within expected limits indicates a healthy battery with low internal resistance. If the voltage dropped significantly (below the recommended cutoff for that battery type), that’s a red flag. For instance, if a 12 V battery falls well below ~10 V under a moderate load, it likely cannot supply the required current or has substantially lost capacity. Also, note the recovery voltage after the load is removed – a healthy battery’s voltage will bounce back close to its normal resting value, whereas a weak battery may recover only partially or very slowly.
- Dung lượng và thời gian chạy: Nếu thử nghiệm tải là một lần xả theo thời gian (ví dụ thử nghiệm 2 giờ ở dòng điện không đổi), hãy sử dụng dữ liệu để tính công suất hiệu dụng. So sánh công suất đo được (or runtime) to the battery’s rated capacity. A significantly lower capacity (e.g. a battery rated for 100 Ah only delivered 60 Ah before hitting cutoff) suggests the battery has aged or deteriorated. Many organizations use an 80% rule of thumb – if a rechargeable battery’s tested capacity falls below ~80% of its original rating, the battery is considered at end-of-life and should be replaced to ensure reliability.
- Điện trở bên trong và độ sụt áp: From the voltage and current data, you can infer the battery’s internal resistance (Ohm’s law: ΔV = I * R_internal). An increasing internal resistance over successive tests is a sign of aging. High internal resistance will cause excessive voltage drop even at moderate loads, leading to poor performance. Some battery testers measure this directly. If you see that even small loads cause a notable voltage dip, the battery likely has a high internal impedance and may fail under heavier loads.
- Nhiệt độ và các bất thường khác: If you recorded temperature, assess whether the battery was heating significantly under load. A rise in temperature during a short test can indicate inefficiencies (energy lost as heat due to internal resistance) or internal cell damage. Any signs of swelling, venting, or leakage observed during or after the test are indicators of a failing battery and a serious reason to remove it from service. In a properly functioning battery, temperature should remain within normal limits for the test’s duration (most of the battery’s energy should be going into the load, not heating the battery itself).
- Xu hướng theo thời gian: One load test provides a snapshot, but multiple tests over a battery’s life can illustrate trends. Keep records of each battery’s test results. If you notice, for example, that each quarterly test shows the voltage under load dropping lower than the last time, or the delivered capacity decreasing gradually, you have a quantified record of the battery’s degradation. This trend analysis allows for predictive maintenance – you can plan to replace batteries trước chúng hỏng hoàn toàn. Trong các hệ thống pin lớn (như hệ thống UPS của trung tâm dữ liệu hoặc ngân hàng lưu trữ năng lượng mặt trời), việc theo dõi các xu hướng này cho từng đơn vị giúp đảm bảo toàn bộ ngân hàng pin vẫn đáng tin cậy bằng cách thay thế các đơn vị yếu kịp thời.
By combining all these observations, you can make an informed judgment about the battery’s health. A good outcome (voltage stable, capacity on target, no excessive heat) means the battery is fit for continued use. Any poor results should prompt further action – perhaps recondition or balance the battery if possible, or retire the battery and replace it to maintain system reliability. Remember that an toàn là trên hết: if a battery shows severe problems (can’t hold voltage, overheats, etc.), remove it from service, as those issues can escalate to complete failure or safety hazards under continued use.
Phần kết luận
Battery load testing is an essential practice for anyone who depends on reliable battery power. By applying realistic loads and scrutinizing how a battery performs, this test provides invaluable insight into the battery’s true state of health that simple voltage readings can’t offer. Regular load testing helps manufacturers ensure product quality and helps users avoid unexpected battery failures by catching early warning signs of degradation. In applications ranging from automobiles to backup power systems, load testing underpins both tối ưu hóa hiệu suất và an toàn, verifying that each battery can meet the demands placed on it. By understanding and implementing proper load testing – following the principles, using the right equipment, and interpreting the results wisely – one can extend battery life, plan timely maintenance, and ensure that critical battery-powered systems remain up and running when they’re needed most.


