When designing power systems for applications ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage, understanding battery metrics is critical. Two fundamental measurements—amp-hours (Ah) and watt-hours (Wh)—determine how effectively a battery will perform in real-world scenarios. At Vade Battery, we specialize in crafting custom lithium-ion battery packs that optimize both metrics for industrial, commercial, and consumer applications. Let’s break down these concepts to help you make informed decisions for your projects.
What Are Amp-Hours (Ah)?
Amp-hours measure a battery’s charge capacity over time. Simply put, 1 Ah equals one ampere of current delivered continuously for one hour. This metric helps engineers estimate runtime for devices or systems. For instance, a 10Ah battery powering a 2A motor will theoretically last 5 hours.
How to Calculate Amp-Hours
The formula is straightforward:
Ah = Current (A) × Time (h).
If a medical device draws 0.5A and operates for 20 hours, it consumes 10Ah (0.5A × 20h = 10Ah). However, this calculation assumes constant voltage, which isn’t always realistic in dynamic applications like robotics or drones.
What Are Watt-Hours (Wh)?
Watt-hours represent a battery’s total energy capacity by factoring in both voltage and current. This metric is indispensable when comparing batteries with different voltages or designing systems where energy efficiency is critical. For example, a 12V 10Ah battery stores 120Wh, while a 24V 5Ah battery also holds 120Wh—demonstrating how higher voltage can achieve the same energy with less current.
How to Calculate Watt-Hours
Use the equation:
Wh = Ah × Voltage (V).
A 7.4V lithium polymer battery with 15Ah capacity delivers 111Wh (15Ah × 7.4V). This calculation is vital for applications like solar energy storage, where total energy output directly impacts system sizing.

Key Differences: Why Both Metrics Matter
While Ah indicates charge capacity, Wh reveals actual energy available for work. Consider these scenarios:
- Voltage Variability: A 36V 10Ah e-bike battery (360Wh) outperforms a 12V 25Ah battery (300Wh) despite lower Ah, because higher voltage reduces energy loss in transmission.
- Application-Specific Demands: Industrial equipment requiring high torque (e.g., forklifts) benefits from high-voltage LiFePO4 packs, while low-power IoT devices prioritize compact 3.6V lithium-ion cells.
For precision, always pair Ah ratings with voltage specifications. Vade Battery’s custom 48V LiFePO4 systems, for example, are engineered to maximize Wh without compromising footprint or safety.
Real-World Applications: Choosing the Right Metric
Solar Energy Storage
Solar installations rely on Wh to match daily energy production with storage needs. A 51.2V 200Ah LiFePO4 battery bank provides 10,240Wh—sufficient to power a small off-grid cabin overnight.
Electric Vehicles
EV manufacturers prioritize Wh/km to estimate range. A 72V 100Ah motorcycle battery (7,200Wh) delivers ~100 km per charge, depending on terrain and load.
Portable Electronics
For devices like drones, Wh determines flight time. A 7.2V 5Ah lithium polymer pack (36Wh) offers longer operation than a 3.6V 10Ah battery (36Wh) due to optimized voltage efficiency.
Why Vade Battery Excels in Energy Solutions
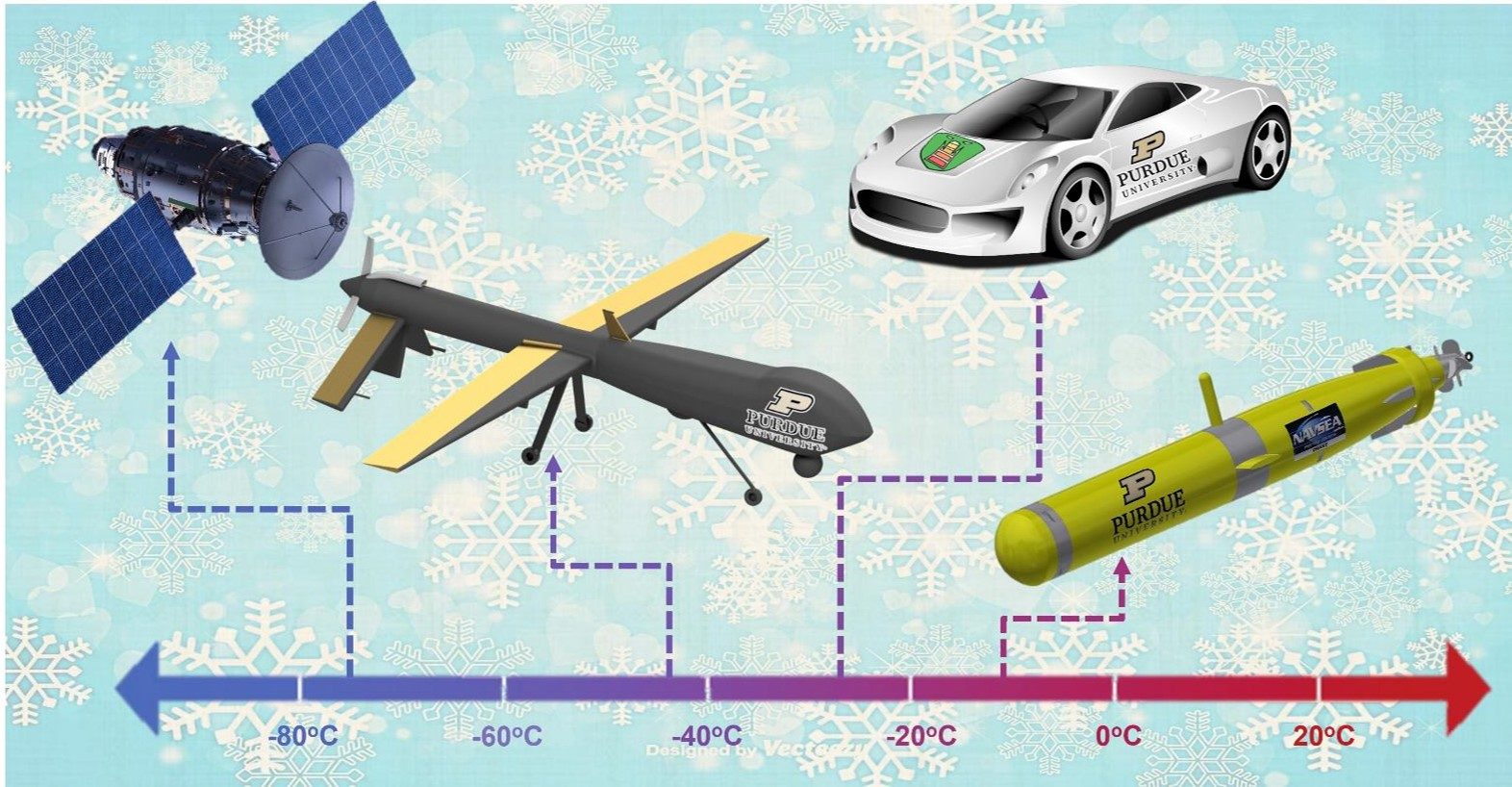
At Vade Battery, we combine ISO-certified safety standards with cutting-edge technology to deliver batteries that excel in both Ah and Wh metrics. Our ultra-low-temperature Li-ion batteries maintain 80% capacity at -40°C, ideal for aerospace or polar research. For high-energy applications, our 18650-based custom packs achieve up to 250Wh/kg, outperforming industry averages by 15%.
Case Study: Marine Navigation Systems
A client needed a 24V battery system resistant to saltwater corrosion with a 10-year lifespan. We engineered a marine-grade LiFePO4 pack delivering 51.8V 200Ah (10,360Wh) with IP67 waterproofing and CAN bus communication.
Final Considerations
Always cross-reference Ah and Wh when selecting batteries. For tailored solutions that balance energy density, voltage stability, and lifecycle costs, explore our custom lithium-ion battery design services. Whether you require a 12V backup system or a 46.8V industrial power module, Vade Battery’s engineers are ready to optimize your energy strategy.
Need a battery that aligns with your technical and budgetary goals? Contact our team for a free consultation.


