¿Qué es la prueba de carga de la batería?
Battery load testing is a diagnostic method for evaluating a battery’s ability to deliver power under real-world operating conditions. It involves applying a controlled electrical load to the battery and observing how the battery’s salida de voltaje y corriente respond. In essence, the test simulates the demands of actual usage – such as starting a car engine or powering a device – and checks whether the battery can maintain an adequate voltage when under load. This is a more stringent test than a simple open-circuit voltage check, since a battery can appear fully charged at rest but No se puede entregar el tiempo de ejecución esperado bajo carga. By performing a load test, engineers and technicians can measure key performance indicators like the voltage drop and internal resistance (which reflects the battery’s capability to supply current). These indicators reveal the true health of the battery and help identify weak or aging batteries before they lead to failure in the field.

Las pruebas de carga de baterías se utilizan ampliamente en industrias donde la fiabilidad de las baterías es crucial. Los mecánicos automotrices realizan pruebas de carga en las baterías de los automóviles (especialmente durante el arranque en frío) para garantizar que proporcionen suficiente corriente para el arranque del motor. En los sistemas de almacenamiento de energía renovable y de respaldo, las pruebas de carga confirman que los bancos de baterías soportarán cargas críticas durante un corte de energía. Fabricantes of batteries and devices also use load tests for quality control – to verify that new battery packs meet their specifications for capacity and output. In consumer electronics and industrial power systems, routine load testing helps catch performance issues early, preventing unexpected downtime or data loss due to a dying battery.
¿Por qué es importante realizar pruebas de carga de la batería?
Las pruebas de carga de baterías son fundamentales para su mantenimiento, seguridad y rendimiento. Algunas razones clave incluyen:
- Control de calidad (fabricantes): La aplicación de pruebas de carga durante la producción garantiza que las baterías cumplan con las especificaciones de diseño y los estándares de calidad. Esto ayuda a detectar defectos de fabricación o desequilibrios en las celdas de forma temprana, evitando que lleguen al mercado baterías de baja calidad. Esto mejora la fiabilidad general del producto y reduce las reclamaciones de garantía.
- Confiabilidad para los usuarios finales: For businesses and individuals who rely on batteries, load testing is crucial to verify that a battery will perform when it’s needed most. For example, backup power systems in telecom or data centers are routinely load-tested to validate battery capacity and runtime. This process can uncover weak cells or wiring issues antes they cause unplanned downtime. By identifying a declining battery in an electric vehicle, solar storage bank, or UPS system, it can be replaced proactively – avoiding sudden failures and ensuring continuous operation.
- Optimización del rendimiento y vida útil: Regular load testing helps in tracking a battery’s available capacity and internal resistance over time. By comparing test results against the battery’s rated capacity, users can determine when the battery has aged significantly. This information allows for optimized charging schedules and timely maintenance. Keeping batteries “exercise tested” under load can also prevent capacity loss from long periods of inactivity, thereby extending their usable lifespan.
- Seguridad y cumplimiento: Faulty or deteriorating batteries can pose safety risks such as overheating, leakage, or in extreme cases (particularly with lithium-ion chemistries) thermal runaway. Load testing under controlled conditions can reveal these issues early, so that unsafe batteries are removed from service. Moreover, many industry standards and transportation regulations require rigorous battery testing. For instance, virtually all lithium-ion batteries must pass the UN 38.3 safety tests – a series of abuse and load conditions – to be certified for transport. Systematically load-testing battery systems helps ensure compliance with such standards and gives confidence that batteries can withstand the stresses of actual use.
Principios de prueba de carga de la batería
En esencia, la prueba de carga de la batería funciona según un principio simple: apply a known load and measure the battery’s response. By observing how much the voltage drops under load and how well the battery sustains the load current, one can infer the battery’s internal condition. A healthy battery will maintain a higher voltage and recover quickly after the test, whereas a weak battery’s voltage will sag significantly under load and may struggle to recover afterward. The amount of voltage drop is directly related to the battery’s internal resistance – lower internal resistance means the battery can deliver higher current with less voltage drop.

Durante una prueba de carga, se controlan de cerca varios parámetros: caída de tensión a través de la batería cuando se aplica la carga, la actual flowing, and often the battery’s temperatura Durante la prueba, una caída de tensión significativa o una generación anormal de calor pueden indicar un aumento de la resistencia interna o daño en las celdas. Por el contrario, una batería en buen estado solo mostrará una caída de tensión leve y un calentamiento mínimo para la carga especificada.
El comportamiento de una batería bajo carga también depende de su composición química y diseño. Los diferentes tipos de baterías tienen características de descarga distintas. Por ejemplo, las baterías de plomo-ácido tienden a presentar una mayor caída de tensión y pérdida de capacidad efectiva a altas tasas de descarga, mientras que las baterías de iones de litio (especialmente las de fosfato de hierro y litio, LiFePO₄) mantienen una tensión más estable y alcanzan un mayor porcentaje de su capacidad incluso bajo cargas elevadas. Esto significa que una batería de litio generalmente soporta mejor el consumo de corriente alta que una batería de plomo-ácido de capacidad equivalente.
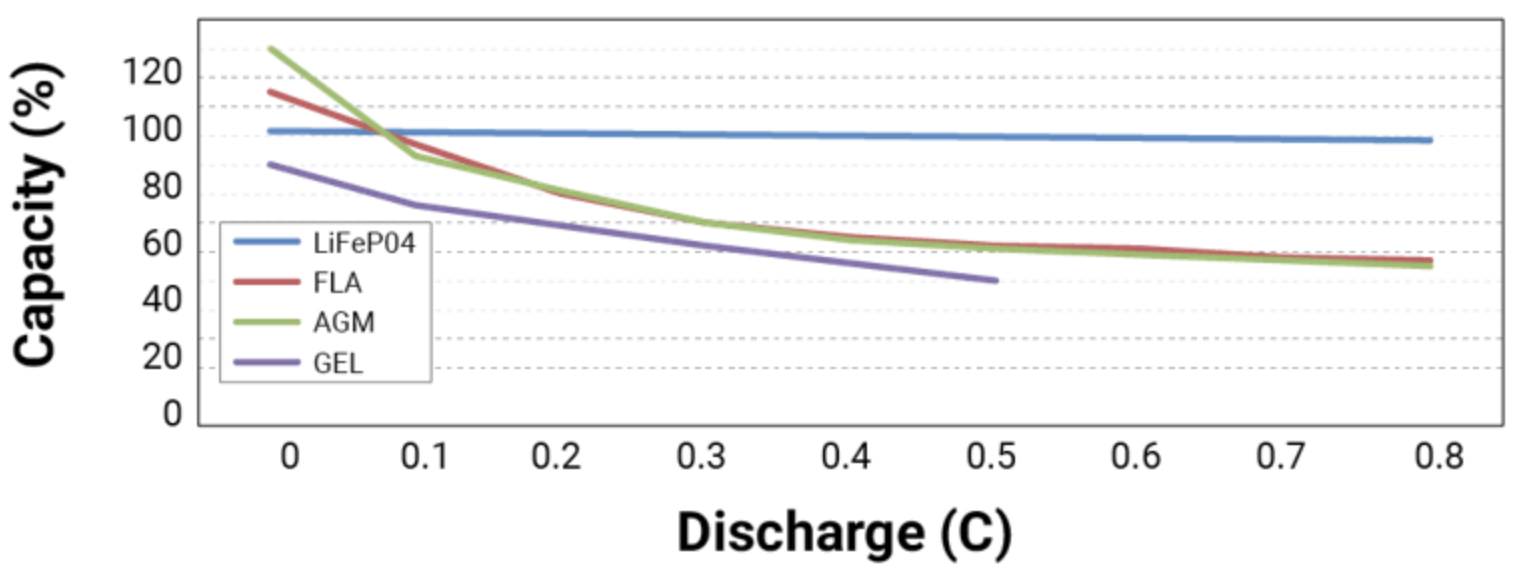
Comprender estas diferencias químicas es importante al interpretar los resultados de las pruebas de carga. Una caída de voltaje que podría ser normal para un tipo de batería podría indicar un problema en otro. Asimismo, una leve Se podría esperar una caída en la capacidad con el tiempo para una batería de plomo-ácido muy utilizada, mientras que un paquete de iones de litio bien administrado debería mantener la mayor parte de su capacidad a través de la misma cantidad de ciclos.
Temperatura is another critical factor influencing load testing. Batteries perform best around room temperature, and both cold and hot conditions can skew test outcomes. In cold environments, a battery’s internal resistance increases and its ability to deliver current decreases – effectively reducing its available capacity. For instance, a battery that provides full capacity at about 27 °C (80 °F) might only deliver roughly 50% of its capacity at –18 °C (0 °F). Importantly, this capacity loss in the cold is usually temporario:una vez que la batería se calienta nuevamente a temperaturas normales, su rendimiento generalmente se recupera a niveles anteriores. Because of this, load tests are usually conducted at standardized temperatures (around 20–25 °C, unless the goal is to specifically test cold/hot performance) to ensure the results reflect the battery’s true health rather than a transient thermal effect.
Para obtener datos precisos y significativos, las pruebas de carga siguen un conjunto de prácticas recomendadas. Las baterías suelen... Probado cuando está completamente cargado and in a rested state (no recent charging or discharging that could skew the voltage). The load applied should be chosen to mimic the battery’s real-world application – for example, drawing a high burst current to simulate a power tool or vehicle starter, or a steady lower current to simulate a device drain. The test is run for a defined duration long enough to observe the battery’s behavior (but usually short enough to avoid completely depleting the battery or causing undue stress). Throughout the test, conditions are kept controlled: the ambient temperature is kept stable, and the test equipment (load banks, meters, etc.) is calibrado for accuracy. Following these principles ensures that the load test results can be reliably compared to manufacturer specifications and previous test results, giving a clear picture of the battery’s state of health.
Tipos de pruebas de carga de batería
Existen varios tipos de pruebas de carga de batería, cada uno adecuado para diferentes propósitos y sistemas de batería:
- Prueba de carga de corriente constante: A steady, fixed current is drawn from the battery for a specified period. By measuring how the battery’s voltage declines over time under this constant load, one can assess its capacity and voltage stability. This is a common method to determine a battery’s true amp-hour capacity – for example, discharging at a 1 C rate (equal to the battery’s rated capacity) and seeing how long it sustains the load before reaching a cutoff voltage.
- Prueba de carga de pulso: The battery is subjected to intermittent high-current pulses separated by rest periods. This tests the battery’s response to sudden power demands. The voltage is monitored during each pulse to see how well it recovers in the brief rest. Pulse testing is often used to evaluate starting batteries or batteries in devices that periodically draw bursts of current. It can also help estimate internal resistance and dynamic performance without fully discharging the battery.
- Prueba de capacidad (tiempo de ejecución): Se trata esencialmente de una prueba de descarga completa controlada. La batería se descarga a una velocidad establecida (que puede ser una corriente constante o un patrón de uso simulado) hasta alcanzar su límite (tensión mínima segura). Se mide el tiempo total o la energía total suministrada. Esto revela... capacidad utilizable de la batería y proporciona una medición directa de la autonomía en esas condiciones. Estas pruebas son útiles para comprobar si una batería aún mantiene la carga esperada. Por ejemplo, una serie de baterías de SAI podría someterse a una prueba de descarga para garantizar que pueda soportar la carga durante el tiempo requerido (p. ej., 30 minutos) antes de que la tensión baje demasiado.
- Prueba de carga de arranque: Used primarily for automotive and lead–acid starter batteries, this test measures the battery’s ability to deliver a very high current for a short duration (as needed to crank an engine). A specialized load tester or carbon pile applies a heavy load (hundreds of amps for a car battery) for 5–10 seconds while monitoring the voltage. The voltage should stay above a specified threshold (e.g. ~9.6 V for a 12 V battery at room temperature, higher if tested warm) during the crank simulation. A battery that cannot maintain voltage under this brief but intense load is likely failing, even if it reads 12 V in open-circuit. Cranking tests are often part of car battery diagnostics, especially in cold weather, to ensure reliable starts.
Equipo de prueba de carga de batería
Para realizar una prueba de carga de forma segura y precisa se requiere el equipo adecuado. Las herramientas y componentes clave incluyen:
- Probador de carga / Banco de carga: This is the device that actually puts a controlled load on the battery. Simple portable load testers for car batteries use a resistor or carbon pile to draw a high current. More advanced electronic load banks can be programmed to draw specific currents or profiles and often include built-in meters. The load tester typically measures the battery’s voltage under load, and some models also measure internal resistance and other metrics.
- Multímetro o voltímetro: A calibrated multimeter is used to independently measure the battery’s voltage and sometimes current during testing. This provides accurate readings and a sanity check against the load tester’s built-in measurements. In some cases, clamp ammeters are also used to verify the exact current being drawn.
- Registrador de datos / Analizador de batería: For more detailed testing (especially in research, manufacturing, or predictive maintenance), data acquisition devices record the battery’s voltage, current, and temperature throughout the load test. The resulting data can be analyzed to see how quickly the voltage declines, how stable the current draw remained, and if there were any irregular drops or recoveries. This is useful for comparing multiple batteries or tracking a battery’s performance over time.
- Sensor de temperatura: Because temperature greatly affects battery behavior, testers often monitor ambient and battery temperature. In critical testing, thermocouples might be attached to the battery to ensure it’s within the desired temperature range and to detect any dangerous overheating during the test.
- Equipo de seguridad: Las pruebas de carga pueden someter a una batería a altas tensiones, por lo que la seguridad es fundamental. Se recomienda el uso de equipo de protección, como guantes aislantes y protección ocular, especialmente con baterías de gran tamaño que podrían liberar chispas o electrolitos si algo sale mal. Se requiere una ventilación adecuada al probar baterías de plomo-ácido (que pueden emitir gas hidrógeno), y se debe disponer de medios de extinción de incendios al probar baterías de litio de alta energía. Además, es importante utilizar cables y abrazaderas con la capacidad nominal correcta para la carga a fin de evitar el sobrecalentamiento durante las pruebas de alta corriente.
Proceso de prueba de carga de la batería
When you are ready to conduct a battery load test, it’s important to follow a structured process:
- Preparación: Begin with a fully charged battery. Make sure the battery has been rested for a while after charging so that the voltage has stabilized (surface charge dissipated). Check the ambient conditions – ideally, test in a room-temperature environment unless you are specifically evaluating cold or hot performance. Gather all required equipment (load tester, multimeter, etc.), and put on appropriate safety gear. Also, review the battery’s specifications to know what load and voltage values to expect (for example, maximum test current or minimum allowable voltage).
- Conectar el equipo: Turn off or set the load tester to zero before connecting. Attach the load tester’s leads to the battery terminals: positive (+) to positive, negative (–) to negative, ensuring solid connections. If using a separate voltmeter or data logger, connect those probes or sensors to the battery as well. Double-check all connections are secure to avoid arcing when the test begins.
- Establecer los parámetros de carga: Configure the load tester to the desired load. This could mean dialing in a certain current (e.g. a 50 A draw for a small battery, or a 300 A draw for a car battery test), or selecting a specific test mode on an electronic load (constant current, pulse, etc.). Refer to the battery’s ratings or the relevant standard for guidance – for instance, use a load equal to half the battery’s CCA rating for an automotive load test, or a 0.2 C (5-hour rate) load for a capacity test, depending on the goal.
- Realizar la prueba: Active el comprobador de carga para que comience a extraer corriente de la batería. Mantenga la carga aplicada durante el tiempo especificado. Esto puede ser de tan solo unos segundos para una prueba de alta corriente, o de minutos u horas para una prueba de descarga prolongada (en cuyo caso, asegúrese de que la carga se mantenga constante o siga el perfil requerido). Monitor the battery’s behavior throughout. Observe the voltage reading – a sharp drop initially is normal, but it should stabilize above the minimum acceptable voltage. Watch for any signs of distress such as the battery overheating, smoking, or emitting unusual odors (if so, terminate the test immediately). If using a data logger, ensure it’s recording properly.
- Monitorear y analizar resultados: Once the test interval is completed, remove or turn off the load. Continue to watch the battery’s voltage recovery for a minute or two. Note the loaded voltage and the recovery voltage. Now analyze the data: Did the battery maintain voltage above the cutoff threshold during the test? How much capacity (Ah or minutes of runtime) was delivered in a full discharge test? Compare these outcomes to the battery’s rated specifications or to previous test results. A healthy battery should meet or come close to its specs (e.g. delivering its rated amp-hours, or keeping above the minimum voltage under load). If the battery’s performance falls short, it may indicate aging or damage. Use this information to decide on next steps – for example, keep the battery in service with a scheduled re-test later, or retire/replace the battery if it failed to perform.
Interpretación de los resultados de la prueba de carga
Comprender el resultado de una prueba de carga de batería es tan importante como realizar la prueba misma. A continuación, se presentan aspectos clave a considerar al interpretar los resultados:
- Respuesta de voltaje: Observe how the battery’s voltage behaved under load. A voltaje estable that stays within expected limits indicates a healthy battery with low internal resistance. If the voltage dropped significantly (below the recommended cutoff for that battery type), that’s a red flag. For instance, if a 12 V battery falls well below ~10 V under a moderate load, it likely cannot supply the required current or has substantially lost capacity. Also, note the recovery voltage after the load is removed – a healthy battery’s voltage will bounce back close to its normal resting value, whereas a weak battery may recover only partially or very slowly.
- Capacidad y tiempo de ejecución: Si la prueba de carga fue una descarga temporizada (por ejemplo, una prueba de 2 horas a una corriente constante), utilice los datos para calcular la capacidad efectiva. Compare capacidad medida (or runtime) to the battery’s rated capacity. A significantly lower capacity (e.g. a battery rated for 100 Ah only delivered 60 Ah before hitting cutoff) suggests the battery has aged or deteriorated. Many organizations use an 80% rule of thumb – if a rechargeable battery’s tested capacity falls below ~80% of its original rating, the battery is considered at end-of-life and should be replaced to ensure reliability.
- Resistencia interna y caída de tensión: From the voltage and current data, you can infer the battery’s internal resistance (Ohm’s law: ΔV = I * R_internal). An increasing internal resistance over successive tests is a sign of aging. High internal resistance will cause excessive voltage drop even at moderate loads, leading to poor performance. Some battery testers measure this directly. If you see that even small loads cause a notable voltage dip, the battery likely has a high internal impedance and may fail under heavier loads.
- Temperatura y otras anomalías: If you recorded temperature, assess whether the battery was heating significantly under load. A rise in temperature during a short test can indicate inefficiencies (energy lost as heat due to internal resistance) or internal cell damage. Any signs of swelling, venting, or leakage observed during or after the test are indicators of a failing battery and a serious reason to remove it from service. In a properly functioning battery, temperature should remain within normal limits for the test’s duration (most of the battery’s energy should be going into the load, not heating the battery itself).
- Tendencias a lo largo del tiempo: One load test provides a snapshot, but multiple tests over a battery’s life can illustrate trends. Keep records of each battery’s test results. If you notice, for example, that each quarterly test shows the voltage under load dropping lower than the last time, or the delivered capacity decreasing gradually, you have a quantified record of the battery’s degradation. This trend analysis allows for predictive maintenance – you can plan to replace batteries antes Fallan por completo. En grandes instalaciones de baterías (como sistemas UPS de centros de datos o bancos de almacenamiento solar), el seguimiento de estas tendencias para cada unidad ayuda a garantizar la fiabilidad de todo el banco de baterías, reemplazando las unidades defectuosas a tiempo.
By combining all these observations, you can make an informed judgment about the battery’s health. A good outcome (voltage stable, capacity on target, no excessive heat) means the battery is fit for continued use. Any poor results should prompt further action – perhaps recondition or balance the battery if possible, or retire the battery and replace it to maintain system reliability. Remember that La seguridad es lo primero: if a battery shows severe problems (can’t hold voltage, overheats, etc.), remove it from service, as those issues can escalate to complete failure or safety hazards under continued use.
Conclusión
Battery load testing is an essential practice for anyone who depends on reliable battery power. By applying realistic loads and scrutinizing how a battery performs, this test provides invaluable insight into the battery’s true state of health that simple voltage readings can’t offer. Regular load testing helps manufacturers ensure product quality and helps users avoid unexpected battery failures by catching early warning signs of degradation. In applications ranging from automobiles to backup power systems, load testing underpins both optimización del rendimiento y seguridad, verifying that each battery can meet the demands placed on it. By understanding and implementing proper load testing – following the principles, using the right equipment, and interpreting the results wisely – one can extend battery life, plan timely maintenance, and ensure that critical battery-powered systems remain up and running when they’re needed most.


