When selecting batteries for industrial, automotive, or consumer applications, understanding the fundamental differences between dry cell and wet cell technologies is critical. At Vade Battery, we specialize in custom rechargeable battery solutions, including advanced lithium-ion and LiFePO4 battery packs tailored to meet global demands. This guide breaks down the technical distinctions, applications, and safety considerations of these two battery types while highlighting how our engineering expertise ensures optimized performance for your projects.
What Is a Dry Cell Battery?
Composition and Structure
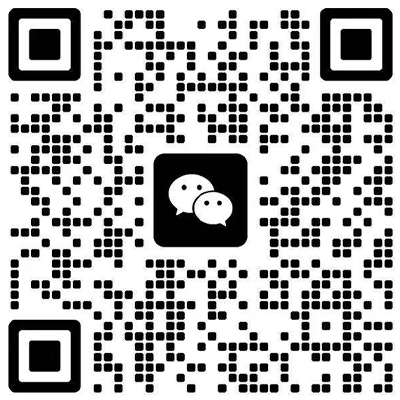
Dry cell batteries use a solid or paste-like electrolyte (typically ammonium chloride or zinc chloride) immobilized in a non-spillable medium. Key components include a zinc anode, manganese dioxide cathode, and a porous separator housed in a sealed metal casing. This design eliminates free-flowing liquids, making them inherently leak-resistant.
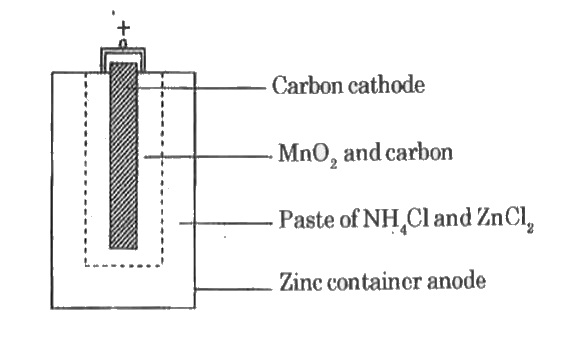
Advantages and Limitations
Dry cells excel in portability and safety, ideal for devices like remote controls, medical equipment, and emergency lighting. Their long shelf life (5–10 years) and minimal maintenance requirements make them cost-effective for low-drain applications. However, they offer lower energy density compared to wet cells, limiting their use in high-power scenarios. Most dry cells are single-use, though rechargeable variants like lithium polymer batteries (found in our Lithium-Ion Battery Pack category) provide sustainable alternatives.
Common Applications
- Consumer Electronics: Remote controls, flashlights, portable radios.
- Medical Devices: Hearing aids, glucose monitors.
- Industrial Tools: Sensors, wireless equipment.

What Is a Wet Cell Battery?
Composition and Structure
Wet cell batteries rely on a liquid electrolyte solution (usually sulfuric acid diluted in water) to facilitate ion transfer between lead plates. The anode and cathode are submerged in this corrosive fluid, housed in a durable plastic casing resistant to chemical degradation.
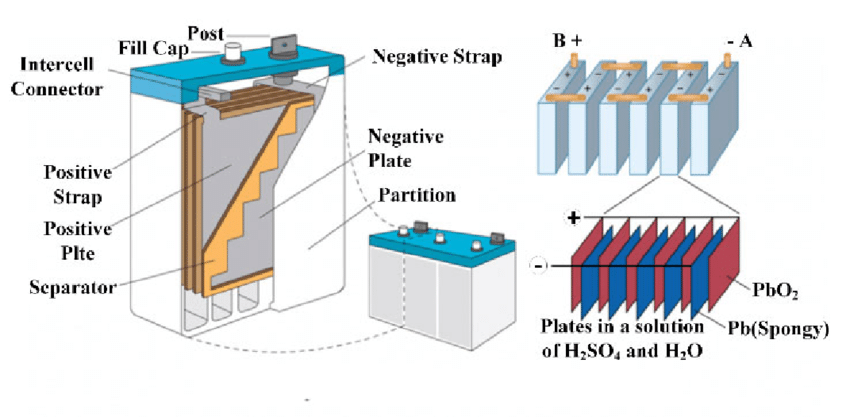
Advantages and Limitations
Wet cells deliver high surge currents, making them indispensable for automotive starters, forklifts, and solar energy storage. Their low cost per watt-hour and recyclability (up to 99% of lead is reusable) appeal to budget-conscious industries. However, they require regular maintenance, including electrolyte refills and terminal cleaning, and pose spill risks if mishandled.
Common Applications
- Automotive: Car, truck, and motorcycle batteries.
- Renewable Energy: Off-grid solar storage systems.
- Industrial Machinery: Forklifts, UPS backup systems.

Key Differences Between Dry Cell and Wet Cell Batteries
1. Electrolyte Type and Safety
Dry cells use immobilized electrolytes, reducing leakage risks and enabling safer operation in portable devices. Wet cells, with liquid electrolytes, demand careful handling to avoid corrosive spills. At Vade Battery, our ultra-low-temperature Li-ion batteries combine the safety of dry cells with extreme-environment performance.
2. Energy Density and Power Output
Wet cells provide higher cranking power (e.g., 600–1000 CCA for car batteries) but lack the energy density of modern lithium-based dry cells. For instance, our 18650 Li-ion cells deliver up to 250Wh/kg, outperforming traditional lead-acid batteries.
3. Maintenance and Lifespan
Dry cells are maintenance-free, whereas wet cells require periodic electrolyte checks. However, advanced AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) wet cells minimize upkeep by trapping electrolytes in fiberglass separators.
4. Cost and Environmental Impact
Wet cells are cheaper upfront but incur higher lifetime costs due to maintenance. Dry cells, especially rechargeable lithium variants, offer longer lifespans and align with eco-friendly initiatives through recyclable designs.
| Feature | Dry Cell Batteries | Wet Cell Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150–250 Wh/kg (e.g., lithium-ion, LiFePO4) | 30–50 Wh/kg (lead-acid) |
| Safety | Low risk: Immobilized electrolyte, leak-resistant | Moderate risk: Liquid electrolyte, spill/acid hazards |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront (e.g., lithium-based) | Lower upfront (lead-acid) |
| Lifetime Cost | Lower (long lifespan, minimal maintenance) | Higher (frequent maintenance, shorter cycle life) |
| Temperature Tolerance | -40°C to 85°C (Ultra-Low-Temp Li-ion) | 0°C to 45°C (standard lead-acid) |
| Recyclability | 95%+ recyclable (Li-ion/LiFePO4) | 99% recyclable (lead-acid) |
| Typical Applications | Medical devices, drones, portable electronics | Automotive starters, forklifts, solar storage |
Notes:
- Cost Efficiency: Wet cells suit budget-focused projects; dry cells excel in long-term ROI.
- Energy Density: Lithium dry cells (e.g., 18650 Li-ion) store 5x more energy than lead-acid wet cells.
- Safety: Dry cells avoid corrosive leaks, critical for sensitive environments.
FAQs
Which is better for high-power applications?
Wet cells are preferred for automotive and industrial uses requiring sudden energy bursts. For sustained, efficient power, lithium-based dry cells (like our 48V LiFePO4 packs) are superior.
Are car batteries wet or dry cells?
Most car batteries are wet cells using liquid electrolytes. However, AGM and lithium alternatives are gaining traction for their maintenance-free operation.
Is a lithium battery dry or wet?
Lithium batteries are classified as dry cells. Their electrolyte is either a gel or liquid absorbed in a separator, preventing leaks.
Why Choose Vade Battery?
At Vade Battery, we engineer custom power solutions that transcend traditional limitations. Whether you need the rugged reliability of wet cells for industrial machinery or the lightweight efficiency of lithium polymer batteries for portable devices, our team optimizes:
- Safety: ISO-certified designs with built-in protection against overcharge and thermal runaway.
- Performance: Batteries tailored to operate in temperatures from -40°C to 85°C.
- Sustainability: Fully recyclable LiFePO4 and lithium-ion chemistries.
For projects requiring specialized voltage configurations, explore our 24V or 72V battery solutions. Ready to start? Submit a custom design request or contact us at service@vadebattery.com.
By understanding the strengths of dry and wet cell technologies, you can make informed decisions for your applications. Trust Vade Battery to deliver precision-engineered power solutions that align with your technical and budgetary needs.


